Extensive Insights right into Concrete Scanning Procedures
Wiki Article
Beyond the Surface: Leveraging Advanced Concrete Scanning Techniques for Unmatched Precision and Insight
Advanced concrete scanning methods have actually emerged as essential devices in this search, supplying a look beneath the surface area to reveal a world of vital insights. By utilizing sophisticated modern technologies, specialists can discover abnormalities, analyze the condition of concrete structures, and make notified decisions that shape the course of projects.Importance of Advanced Concrete Scanning
The importance of utilizing sophisticated concrete scanning methods exists in the exceptional precision they use for finding sub-surface abnormalities and making certain structural honesty. By using advanced technologies such as ground-penetrating radar (GPR), electro-magnetic induction, and progressed sonar imaging, building and construction experts can dig beneath the surface of concrete structures with a level of accuracy that far exceeds traditional inspection techniques. Concrete Scanning. These strategies enable the recognition of covert dangers like rebar deterioration, gaps, avenues, or post-tension wires that can compromise the stability and safety and security of a structure with timeFurthermore, progressed concrete scanning offers very useful understandings into the general problem of a concrete aspect without the demand for intrusive steps, lessening the risk of creating damages throughout the assessment procedure. The capability to identify the exact area and deepness of potential issues permits targeted repair work and upkeep, ultimately prolonging the lifespan of the framework and maximizing its efficiency. In significance, the value of innovative concrete scanning can not be overstated in the world of building and framework upkeep, where accuracy and dependability are critical.
Kinds Of Cutting-Edge Technologies
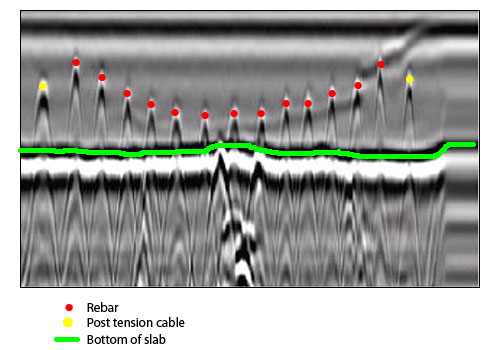
Abnormalities and Flaw Discovery

In addition to GPR, concrete scanning methods like thermography and impact-echo testing are additionally reliable in finding defects and abnormalities. By leveraging these innovative methods, experts can proactively resolve structural problems, ensuring the longevity and safety and security of concrete frameworks.
Assessing Concrete Problem
Just how can engineers precisely review the problem of concrete structures to ensure their durability and safety? Numerous advanced concrete scanning strategies are used for this purpose. Ground-penetrating radar (GPR) is commonly used to analyze the inner framework description of concrete, identifying spaces, splits, and other abnormalities that might compromise its stamina.Moreover, visual evaluation remains an essential component of concrete condition assessment. Engineers aesthetically examine the surface for indicators of degeneration, such as spalling, fracturing, or discoloration. Combining non-destructive screening techniques with visual assessments enables an extensive assessment of concrete problem, making it possible for designers to determine potential concerns early and execute prompt maintenance or fixings. By leveraging these advanced strategies, engineers can guarantee the lasting longevity and security of concrete structures.
Enhancing Decision-Making Procedures
In the realm of infrastructure administration, optimizing decision-making procedures is imperative for ensuring the reliable upkeep and long life of concrete structures. Improved decision-making procedures in concrete monitoring entail utilizing sophisticated scanning methods to collect detailed information on the condition of frameworks. By leveraging innovations such as ground-penetrating radar and 3D imaging, stakeholders can make educated decisions regarding support, fixing, or replacement approaches.These progressed scanning strategies offer indispensable insights into the inner structure of concrete, determining potential issues such as spaces, splits, or corrosion that may not show up on the surface area. This level of comprehensive details enables positive maintenance preparation, reducing the threat of structural failings and raising the general lifespan of concrete frameworks.
In addition, by integrating electronic documents and evaluation devices into the decision-making procedure, stakeholders can track the advancement of concrete problems over time, making it possible for predictive go to this site upkeep techniques and maximizing source allowance. Ultimately, the integration of innovative concrete scanning techniques boosts decision-making procedures by providing unmatched accuracy, understanding, and effectiveness in facilities administration.
Conclusion
In conclusion, progressed concrete scanning methods use exceptional accuracy and insight in detecting abnormalities, flaws, and analyzing the condition of concrete structures. By leveraging cutting-edge modern technologies, decision-making procedures can be enhanced, leading to more effective and enlightened solutions for preserving and fixing concrete infrastructure. These techniques play an essential function in ensuring the safety and security and durability of concrete frameworks, making them an indispensable tool in the area of construction and design.Additionally, advanced concrete scanning supplies very useful insights right into the overall problem of a concrete component without the need for intrusive procedures, lessening the threat of triggering damages during the analysis procedure - Concrete Scanning. One more cutting-edge technology is 3D X-ray scanning, which supplies comprehensive images of the inner structure of concrete, providing important details without the need for destructive testing. Furthermore, Concrete Cover Meters are image source utilized to determine the thickness of concrete cover over reinforcement bars precisely. Enhanced decision-making processes in concrete monitoring entail making use of innovative scanning strategies to gather detailed information on the problem of frameworks.In final thought, advanced concrete scanning strategies provide exceptional accuracy and understanding in spotting abnormalities, defects, and examining the condition of concrete frameworks
Report this wiki page